A virtual servers is a computer operating system and software that runs on a physical server. This type of machine is very similar to a physical server, but it’s not the same. In addition to being able to run your application software and infrastructure on their own, virtual servers can be managed differently than physical ones.
The main reason you want to think of this option over traditional hardware is that you’ll be able to manage your infrastructure without having to worry about purchasing new hardware or dealing with maintenance issues. This guide will provide an overview of what virtual servers are and how they differ from traditional servers; as well as why you may want one for your organization’s needs.
Virtual servers are a powerful tool for businesses to boost their performance and efficiency. They can be used to host various applications, from streaming video services to e-commerce sites.
Virtual servers are also a great way for companies that have limited resources but need high-quality solutions for their customers.
For example, if you’re launching your online store or handling client requests via phone calls every day, then it would be difficult if not impossible for everyone involved in the project (including yourself) unless they had access to physical servers located somewhere else away from where all this work happens!
What is a virtual server?
A virtual server is a software-based server that runs on a physical server. The virtual machine is separate from the physical one, but it can use all of the resources and be managed by the same hardware.
There are many benefits to using virtual servers:
They provide greater flexibility in how you set up your organization’s IT infrastructure. You can run multiple applications or services on different servers without having to purchase additional hardware or rack space for each new project.
They allow organizations to save money by reducing their total cost of ownership (TCO) over time because they don’t require as much capital investment upfront—they’re cheaper than buying new equipment every few years!
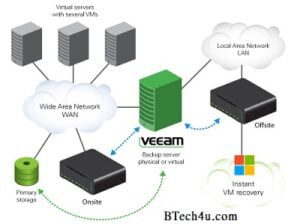
Advantages of virtual servers
One of the greatest advantages of virtual servers is their ability to reduce hardware costs. Virtual servers do not require as much physical space or energy as physical servers do. As a result, you can purchase fewer boxes at once and save money on your budget.
Virtual server management also provides greater flexibility than physical servers because it allows you to scale up or down based on demand without having to worry about adding more hardware or purchasing new ones to accommodate changes in traffic volume or other factors that might arise from time to time (e.g., new employees joining an organization). This increased flexibility means that your organization will have better control over its data center environment and be able to meet changing demands without having wasted resources trying out different solutions before finding something suitable for everyone involved!
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing is a way to access computing resources without having to buy your hardware. It’s also known as “infrastructure as a service,” or IaaS, because it provides access to servers and storage, rather than the actual physical servers themselves.
Cloud computing offers several benefits over traditional on-premise deployments:
You can pay for services you use rather than buying them outright. This means no need to purchase expensive equipment like racks full of servers; instead, all you need is Internet connectivity and power (and maybe some space).
Cloud providers offer scalability—meaning they can scale up or down according to demand—so you never have to worry about being stuck with more capacity than needed at any given time.*
Differences in physical and virtual servers
The main difference between physical and virtual servers is the underlying platform. Physical servers are hardware-based while virtual machines are software-based. This means that you can move your entire application environment from one server to another without having to reboot or reinstall it—a process known as “moving” a VM (virtual machine).
In addition, VMs are more flexible and scalable than their physical counterparts because they have no limitations on their size or hardware requirements; however, this also means that there’s no guarantee that your VMs will run as efficiently on different hosts within an environment as they would if they were running directly from a single host like other types of hosting solutions such as cloud hosting providers do today!
You may also like: Services From The Internet: Transforming Our Daily Lives
How to choose the right type of server for your needs
When selecting the right type of server for your needs, there are three main factors that you should consider. First, whether or not you require full power over hardware. Suppose you are moving to running virtualized applications or operating systems on the engine and want to ensure that they work as expected. In that case, a physical server is probably not going to be ideal for your needs.
Secondarily, do you need flexibility?
This refers to how easy it would be for someone else who isn’t familiar with your organization’s IT infrastructure (or even its software) to scale up their usage if needed—something that could get tricky when dealing with cloud servers since they’re often only accessible through an API rather than having dedicated IP addresses like traditional ones do; this means that scaling up becomes more difficult without knowing exactly what’s going on behind those APIs themselves! Finally: thirdly—and most importantly—does this fit within budget constraints?”
Virtual servers
Virtual servers can help you save time and money by freeing you up to focus on the things that matter most. You might be concerned about the amount of space your data center is taking up or the amount of power it needs, but these are just two possible costs. By using virtualization, these concerns may not be as important because:
You’ll have more flexibility in terms of how much space your servers take up; this means that if there’s a need for expansion later on, it won’t require any additional investment in hardware or software upgrades (which could otherwise cost thousands).
Your power bills will also be reduced significantly because virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently without having to add extra hardware like cooling units or fans (which would otherwise require maintenance).
Related: Masterful Drone Training: The Thrilling Adventurer In You
Conclusion
Virtual servers have many advantages over physical servers. They take up less space, they’re easier to handle and maintain, and they can be managed from anywhere in the world. If you are looking for a cost-effective way to expand your business while still keeping up with ever-changing technology trends, then virtual servers might just be what you need!
To read top stories click here






Add comment